Vespa 125 GTR (VNL2T)
In 1969 the GT125 becomes the GTR 125, retaining the same chassis prefix (VNL2T).Within the construction period of the GTR models, a technical change takes place 'under the bonnet', away from the old 2-channel engines to the modern technology coming PX 3-channel engines.Parallel to the Sprint150 models, where the same cautious modernisation took place while retaining the outer visual appearance, the GTR125 is the version for the 125cc class.
OPTICS
Instead of the trapezoidal headlamp, the handlebars with large round headlamp also used on upcoming vehicles such as the Rally, Sprint Veloce and TS are now fitted. This also means that the speedometer shape changes from shell-shaped to the somewhat smaller design of the Rally and Primavera models. In addition, the tail light has already been changed to the more modern type of the Rally200 models. It is now completely made of plastic and has a plastic cover on top, which is black on the GTR models. The lettering has also changed. At the rear, instead of a lettering in stylised handwriting, a square frame with block letters (125 g.t.r.) is used as on the Rally models. The vehicle colours and the colour of the side cover rubbers also change. Otherwise, everything remains visually the same as on the previous GT models.
TECHNIQUE
The engine technology of the GTR125 has its roots in the old-fashioned power unit of the first large frame engines with rotary intake control, as presented with the introduction of the VNB models.
This means a 'flying' bearing of the crankshaft in two equally sized crankshaft bearings (these are not held in place by snap rings but only by the oil seals in the engine casing). The engine has only two overcurrent channels in the cylinder as well as in the engine casing (hence the general designation 2-channel engine). Furthermore, the first series still have a multi-part wheel bearing on the gear shift side. Also, the first engine generations still have a shifting cross with a bar and a split shifting bolt. The SI20/17 carburettor used at the beginning is replaced by a more powerful SI20/20D (as in the later PX125-150 models).
The most important change comes with the change of the crankshaft type and the associated change of the crankshaft bearing. From chassis no. 145901 onwards, a crankshaft was used, which was also used in the later PX models. At the same time, the bearing on the alternator side was changed from the large drawing bearing 613912 to a standardised industrial needle bearing type NBI. On the clutch side, the crankshaft bearing was not changed, but it was now fixed by a circlip and the oil seal now sits in front of the bearing (seen from the inside of the crankcase). The clutch-side crankshaft bearing is therefore now lubricated by the gearbox oil, no longer by the two-stroke mixture.
An important advantage of this new design was that the crankshaft could no longer move when the clutch was operated. The crankshaft stump was also much stronger, so that it was virtually impossible for the stump to break off at increased engine power. This was also accompanied by a larger cone for the pole wheel, which was still operated by a contact ignition. The same ignition base plate was later used in the P125X models (without indicators, Italy).
This change was also accompanied by the change to the clutch type of the PX models. Basically identical to that of the Sprint models, the overall height was changed here.
Milestones in the engine history of the GTR 125 models
From frame number 124014: Change of gearshift cross and gearshift pin to old PX type.
from frame number 138957 (vehicles with battery): conversion from 2-channel to 3-channel technology (cylinder and engine housing)
From frame number 145901: Changeover from pressure spring kick starter pinion to spiral spring (previously leaf spring)
from frame number 145901: Changeover to crankshaft type, crankshaft bearing, oil seals, clutch of PX models
from frame number 145901: Conversion of pole wheel, ignition
from frame number 151279: Conversion of carburettor from SI20/17 to SI20/20 (vehicles with battery were already converted from frame number 138957)
up to frame number 151592: gearshift detent type Sprint
Frame numbers according to year of construction
1968: VNL2T 100001-100751
1969: VNL2T 100752-107340
1970: VNL2T 107341-112891
1971: VNL2T 112892-117898
1972: VNL2T 117899-124092
1973: VNL2T 124093-128068
1974: VNL2T 128069-135902
1975: VNL2T 135903-141381
1976: VNL2T 141382-145658
1977: VNL2T 145659-149641
1978: VNL2T 149642-151788
Original paint (MaxMeyer)
Body:
Chiaro Di Luna Metallizato
PIA108 (1.268.0108) |
 |
from 1971 on:
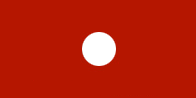
Rosso Corallo
PIA811 (1.298.5811) |
 |
from 1972 on:
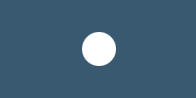
Blu
PIA230 (1.298.7230) |
 |
from 1973 on:
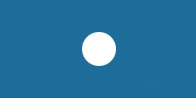
Azzurro Cina
PIA8/1 (1.298.7402) |
 |
Grigio Polaris Metallizato
PIA200 (1.268.8200/8010M) |
 |
Primer:
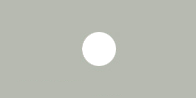
Grigio (Antiruggine)
PIA8012M (8012M) |
 |
Mounting parts:
Alluminio
PIA983 (1.268.0983) |
 |








